Use cases
EDB Postgres Distributed for Kubernetes was designed to work with applications that reside in the same Kubernetes cluster for a full cloud native experience.
However, it might happen that, while the database can be hosted inside a Kubernetes cluster, applications can't be containerized at the same time and need to run in a traditional environment such as a VM.
The following is a summary of the basic considerations. See the EDB Postgres for Kubernetes documentation for more detail.
Case 1: Applications inside Kubernetes
In a typical situation, the application and the database run in the same namespace inside a Kubernetes cluster.
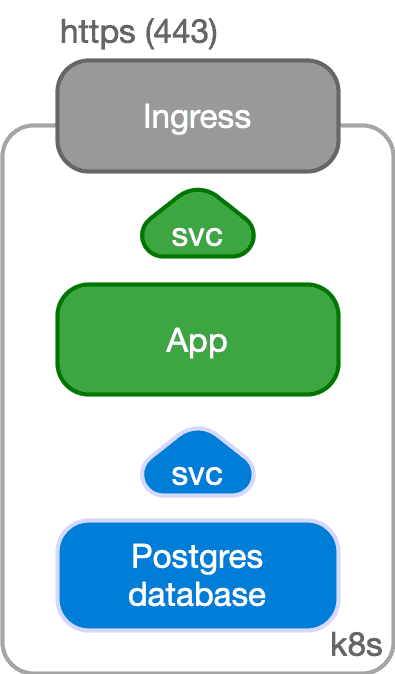
The application, normally stateless, is managed as a standard deployment, with multiple replicas spread over different Kubernetes nodes and internally exposed through a ClusterIP service.
The service is exposed externally to the end user through an Ingress and the provider's load balancer facility by way of HTTPS.
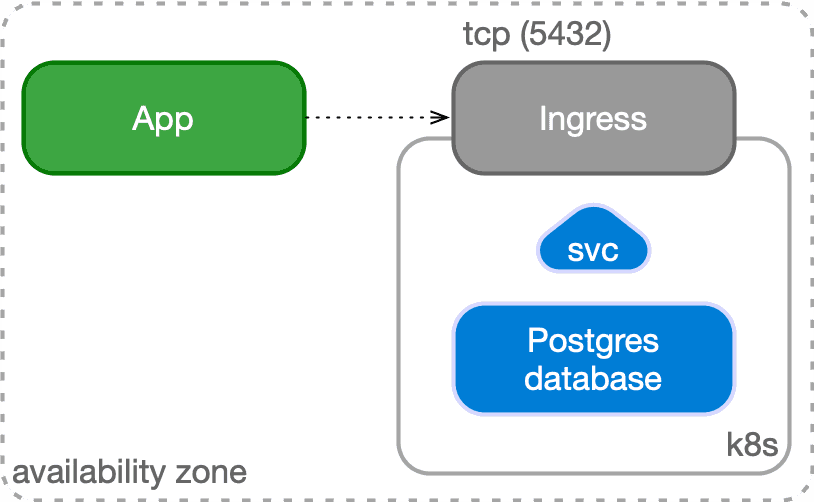
Case 2: Applications outside Kubernetes
Another possible use case is to manage your PGD database inside Kubernetes while having your applications outside of it, for example, in a virtualized environment. In this case, PGD is represented by an IP address or host name and a TCP port, corresponding to the defined Ingress resource in Kubernetes.
The application can still benefit from a TLS connection to PGD.